Selecting the right anti-static coated panel is critical when we discuss about ESD sheets applied in electrostatic-sensitive environments,for examples,electronics manufacturing, medical clean-room, and chemical plants. Polycarbonate (PC), PVC, and acrylic (PMMA) are three widely used materials, but their performance differences directly impact cost, longevity, and applications. This article breaks down the science behind material selection, from technical specs to real-world use cases.
Material Performance: Impact Resistance, Transparency, and Temperature Tolerance
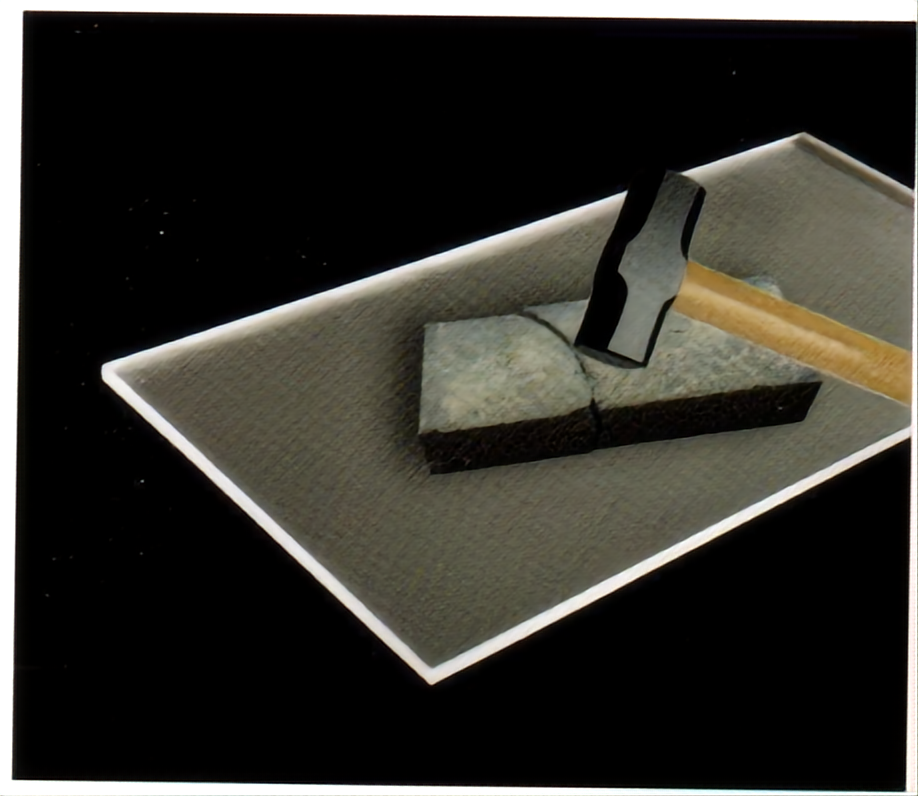
1. Polycarbonate (PC) Panels: The Impact-Resistant Guardian
Impact Strength: 200x stronger than glass, PC panels won't shatter even under severe collisions, earning the title of "explosion-proof king."
Temperature Range: Stable in extreme conditions (-40°C to 120°C), ideal for high-temperature workshops or cold storage.
Weakness: Prone to surface scratches; requires anti-abrasion coatings.
Typical Applications
Explosion-proof equipment windows, aerospace instrument panels, high-precision lab shielding.
2. PVC Panels: Budget-Friendly Workhorse
Chemical Resistance: Withstands acids, alkalis, and most solvents, perfect for chemical processing zones.
Flexibility: Easily bent and cut into complex shapes (e.g., custom electronic packaging trays).
Weakness: Limited temperature tolerance (-10°C to 60°C); warps under heat and degrades outdoors.
Typical Applications
Lab anti-static mats, temporary dust barriers, low-cost electronic component trays.
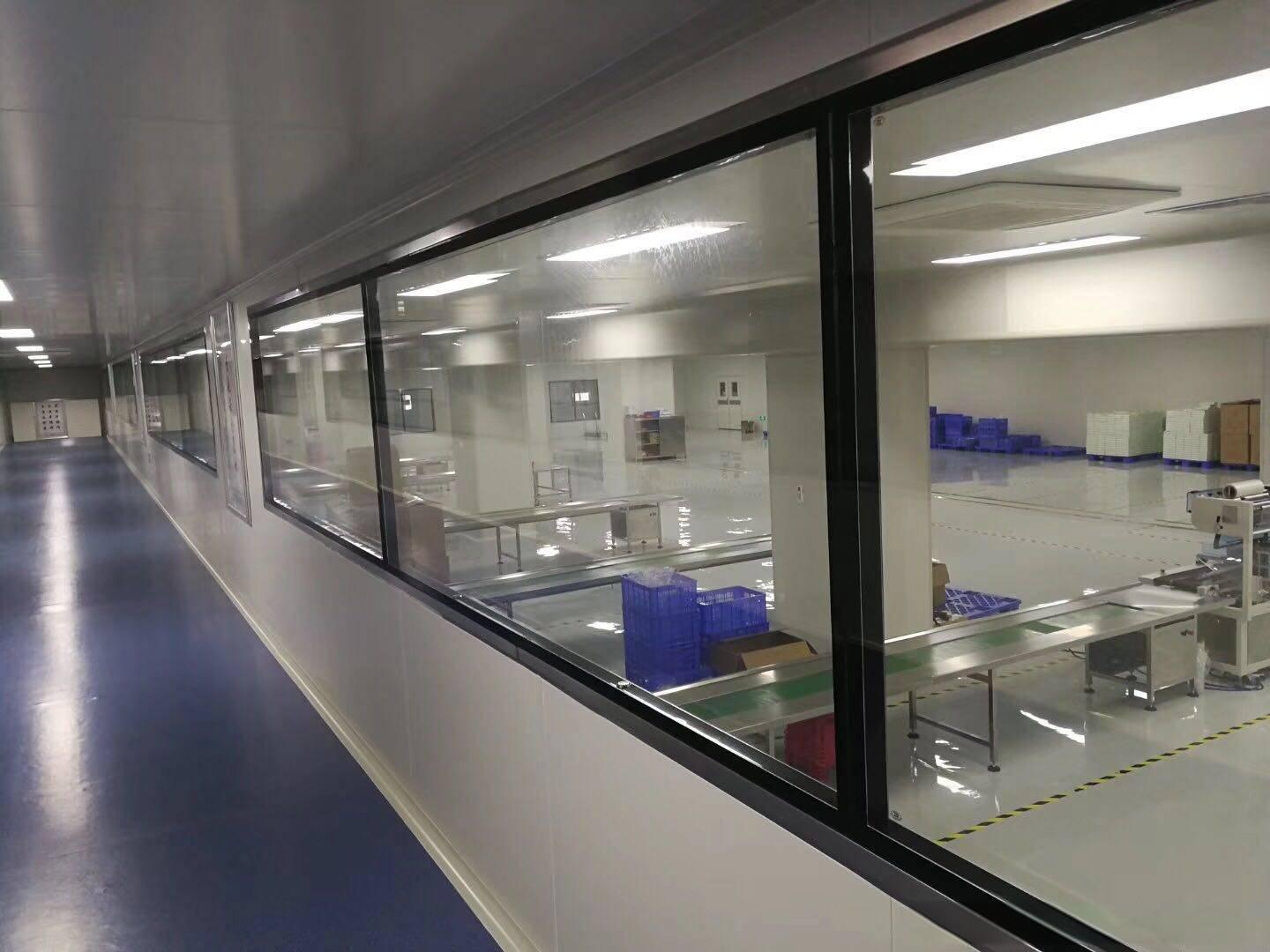

3. Acrylic (PMMA) Panels: Clarity Champion
Optical Performance: 92% light transmittance (near-glass clarity) with high surface hardness (Mohs hardness level 3-4).
Mach-inability: Easily engraved, polished, and shaped into precision display panels.
Weakness: Brittle (cracks under impact),yellows outdoors without UV-resistant additives.
Typical Applications
Medical cleanroom windows, advertising lightboxes, anti-static display covers.
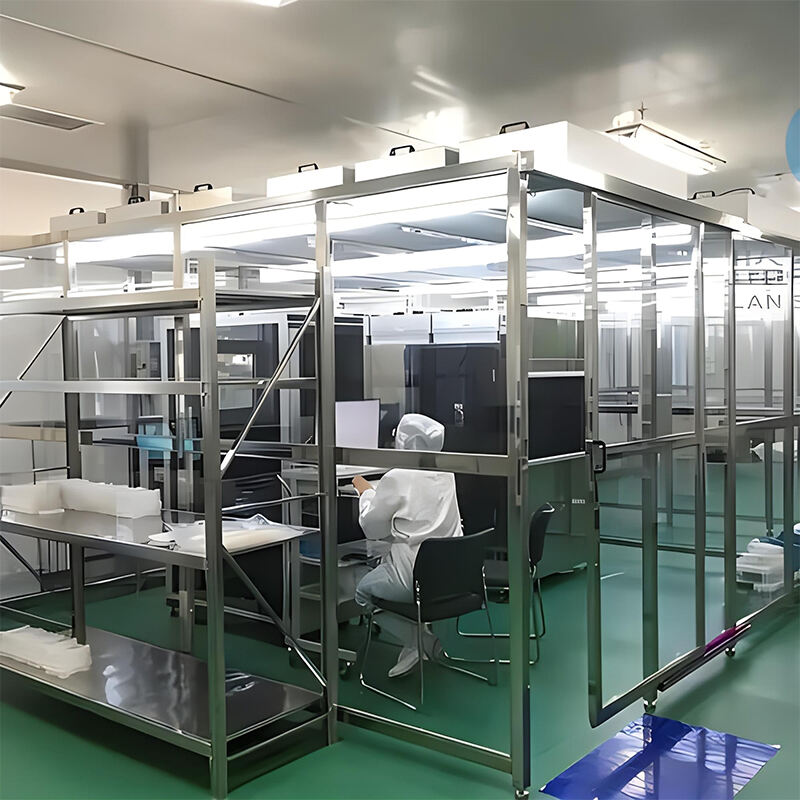

Environmental Suitability
Polycarbonate (PC) Panels: These are well-suited for environments with extreme temperatures or high levels of ultraviolet (UV) exposure.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Panels: It is advisable to use PVC panels in settings that do not involve high temperatures or humidity.
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) Panels: PMMA panels should be kept away from organic solvents, as these substances can potentially damage the surface.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of anti-static coatings, particularly to prevent oil residues from diminishing conductivity. In terms of wear resistance, PC and PMMA coatings perform better than PVC, thereby reducing maintenance costs over time.
Decision Guide: How to choose the right ESD Sheet
| Application | Best Material | Key Reason |
| High-impact + extreme temps | Polycarbonate | Unmatched durability |
| Short-term + low-cost ESD | PVC | Affordability & flexibility |
| High clarity + precision | Acrylic | Glass-like optics & finish |
Choosing anti-static panels isn't about picking the most expensive option—it's about aligning material strengths with your operational needs. Whether prioritizing budget for electronics workshops or optical perfection for medical clean rooms, understanding these materials ensures cost-effective, long-term performance.
Need a tailored solution? Contact our materials engineering team for expert support!

